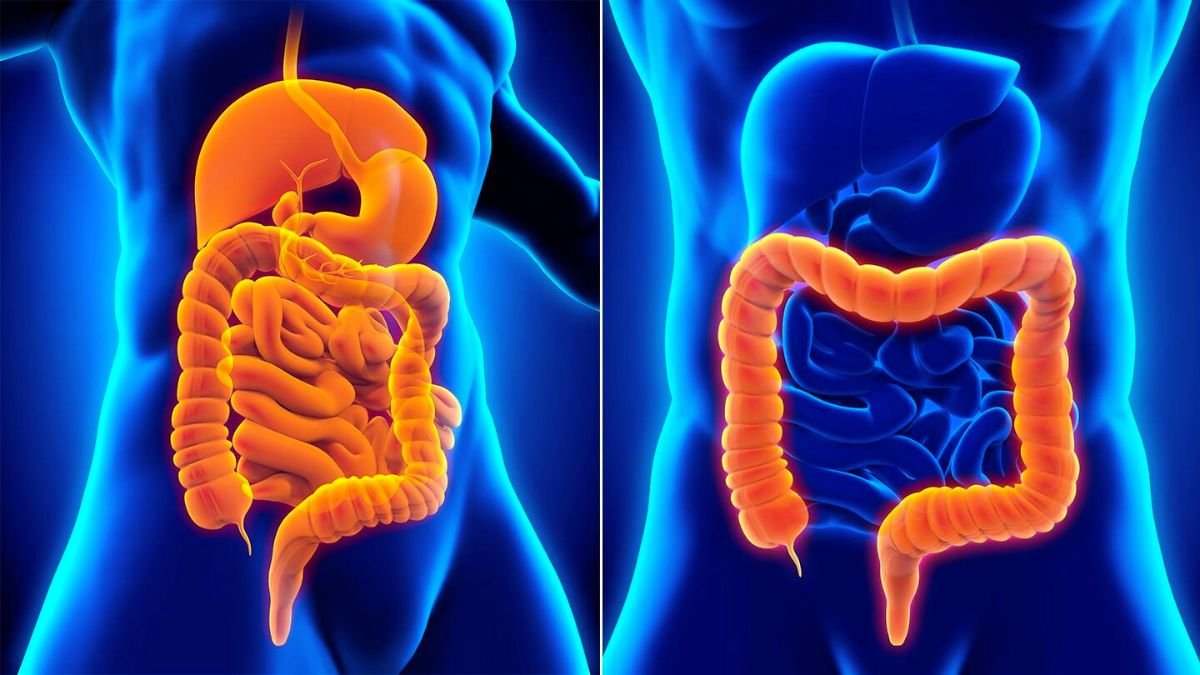
Difference between Ulcerative Colitis and Crohn’s Disease
Difference between Ulcerative Colitis and Crohn’s Disease are two types of chronic inflammatory bowel diseases that affect the gastrointestinal tract. Although they share similarities in terms of symptoms and treatment, there are key differences that distinguish them. Understanding these differences is crucial for proper diagnosis and management. In this article, we will explore the characteristics, symptoms, and treatment options for both conditions, highlighting their distinctions.
Overview of Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis primarily affects the colon (large intestine) and rectum. It is characterized by chronic inflammation and ulcers in the inner lining of the colon. The exact cause of ulcerative colitis remains unknown, but it is believed to involve an abnormal immune response.
Symptoms
Common symptoms of ulcerative colitis include:
- Abdominal pain and cramping
- Persistent diarrhea, often with blood or mucus
- Rectal bleeding
- Urgency to have a bowel movement
- Fatigue
- Weight loss
Diagnosis
To diagnose ulcerative colitis, healthcare providers may perform various tests, including colonoscopy, sigmoidoscopy, blood tests, and imaging studies. These tests help evaluate the extent and severity of inflammation in the colon.
Treatment options
The treatment for ulcerative colitis aims to reduce inflammation, manage symptoms, and achieve remission. Medications such as anti-inflammatory drugs, immunosuppressants, and biologics are commonly prescribed. In severe cases, surgical removal of the colon (colectomy) may be necessary.
Overview of Crohn’s Disease
Crohn’s disease can affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract, from the mouth to the anus. It involves chronic inflammation that extends through the entire thickness of the affected area. The exact cause of Crohn’s disease is also unknown, but it is thought to involve a combination of genetic, environmental, and immune system factors.
Symptoms
The symptoms of Crohn’s disease can vary depending on the location and severity of the inflammation. Common symptoms include:
- Abdominal pain and cramping
- Diarrhea
- Fatigue
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss
Diagnosis
Diagnosing Crohn’s disease requires a combination of medical history, physical examination, laboratory tests, imaging studies, and endoscopic procedures such as colonoscopy or capsule endoscopy. These tests help identify the affected areas and determine the extent of inflammation.
Treatment options
The treatment for Crohn’s disease focuses on reducing inflammation, controlling symptoms, and preventing complications. Medications such as anti-inflammatory drugs, immunosuppressants, antibiotics, and biologics are commonly used. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove the affected portion of the digestive tract or manage complications.
Key Differences between Ulcerative Colitis and Crohn’s Disease
While both ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease are inflammatory bowel diseases, there are several key differences between them:
- Location of inflammation: Ulcerative colitis only affects the colon and rectum, whereas Crohn’s disease can involve any part of the digestive tract, from the mouth to the anus.
- Affected areas of the digestive tract: Ulcerative colitis involves continuous inflammation starting from the rectum and extending to the colon in a continuous manner. In contrast, Crohn’s disease can cause skip lesions, meaning it can affect different areas of the digestive tract with healthy sections in between.
- Types of inflammation: Ulcerative colitis involves inflammation limited to the inner lining of the colon, while Crohn’s disease can result in inflammation that extends through the entire thickness of the affected area.
- Complications: Ulcerative colitis is associated with an increased risk of developing colon cancer, whereas Crohn’s disease can lead to complications such as bowel obstructions, ulcers, fistulas, and abscesses.
Similarities between Ulcerative Colitis and Crohn’s Disease
Despite their differences, ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease also share some similarities:
- Both conditions are chronic and involve inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract.
- They can cause similar symptoms such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, and weight loss.
- Treatment approaches for both conditions often include medications to control inflammation and manage symptoms.
- Both conditions may require surgery in severe cases or to address complications.
Conclusion
In summary, ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease are two distinct forms of inflammatory bowel disease with similar symptoms but different characteristics. Ulcerative colitis primarily affects the colon and rectum, while Crohn’s disease can involve any part of the digestive tract. Understanding the differences between these conditions is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective management. If you experience persistent gastrointestinal symptoms, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and guidance.
FAQs
1. Can diet affect the symptoms of ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease? Diet can play a role in managing the symptoms of ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. While there is no one-size-fits-all approach, certain dietary modifications, such as avoiding trigger foods, incorporating anti-inflammatory foods, and ensuring adequate nutrient intake, may help alleviate symptoms.
2. Are ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease hereditary? Both ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease have a genetic component, but they are not directly inherited. Having a family history of these conditions can increase the risk, but environmental factors and the immune system also play significant roles.
3. How can stress impact ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease? Stress does not cause ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease, but it can exacerbate symptoms or trigger flare-ups. Stress management techniques such as exercise, meditation, and counseling may help reduce the impact of stress on these conditions.
4. Are there any natural remedies for managing these conditions? While natural remedies cannot cure ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease, some individuals find relief from certain complementary therapies. These may include probiotics, herbal supplements, acupuncture, and mind-body practices. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional before trying any natural remedies.
5. Is it possible to lead a normal life with ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease? With proper management, many individuals with ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease can lead fulfilling lives. It may require a combination of medications, lifestyle adjustments, regular monitoring, and support from healthcare professionals. Each person’s experience with these conditions is unique, and finding the right treatment plan is crucial for maintaining quality of life.